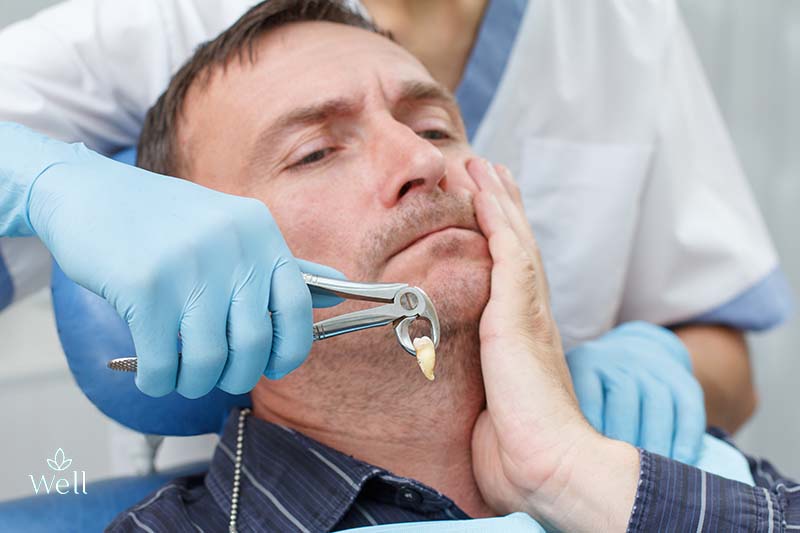
When it comes to maintaining oral health, gum disease is one of the most common issues that both men and women over the age of 45 in the USA encounter. Understanding how to treat this condition is crucial for preventing more severe health problems down the line. In this article, we’ll explore what kind of dentist treats gum disease, the types of treatments available, and how to seek the right help for your gum health.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, refers to infections of the structures surrounding the teeth. The most common types include gingivitis and periodontitis. Recognizing the symptoms early on can lead to effective treatment and a healthier smile. Common symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Pain when chewing
- Loose teeth
- Changes in bite or tooth alignment
Who Treats Gum Disease?
The primary focus of treating gum disease falls to two main types of dental professionals:
- General Dentists: These are the most commonly visited dental professionals. They are trained to recognize, diagnose, and manage early stages of gum disease. General dentists perform cleanings and provide treatment for gingivitis. However, their capabilities may be limited when it comes to more advanced cases of gum disease.
- Periodontists: For patients with moderate to severe gum disease, a periodontist—a dentist specialized in the diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease—becomes essential. They receive additional training to understand the complex nature of gum issues and are skilled in performing surgical interventions when necessary.
Types of Treatments for Gum Disease
Treatment options for gum disease vary depending on the severity of the condition:
1. Professional Cleanings
A basic approach for treating gum disease involves professional dental cleanings, which can effectively remove plaque buildup and reduce inflammation in the gums. This is typically performed by a general dentist.
2. Scaling and Root Planing
For patients with more advanced gum disease, scaling and root planing is a deeper cleaning method performed by either a general dentist or a periodontist. This procedure involves:
- Removing plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line
- Cleaning and smoothing the roots of the teeth to promote healing
3. Medications
In combination with other treatments, dentists may prescribe antibiotics to help eliminate bacterial infections associated with gum disease. These can come in the form of:
- Topical gels
- Oral antibiotics
4. Surgical Treatment
For severe cases, surgical intervention might be necessary. Treatments may include:
- Flap Surgery: This procedure involves lifting back the gums to remove tartar and then suturing the gums back in place.
- Bone Grafting: If the bone supporting the teeth has been destroyed, grafting can restore the structure.
- Tissue Grafting: For areas where gums have receded, grafting can help regenerate tissue.
Choosing the Right Dentist
Choosing the right dental professional is vital for effective gum disease treatment. Consider the following factors:
- Qualifications: Ensure the dentist is accredited and has specialized training in periodontal care.
- Experience: Look for a dentist with a proven track record in treating gum disease.
- Patient Reviews: Check online reviews or ask for referrals to gauge patient satisfaction.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than cure. Some effective strategies include:
- Practicing good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day and flossing daily.
- Regular dental check-ups to monitor gum health.
- Avoiding tobacco products, which can impair gum health.
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and nutrients beneficial for gums.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of gum disease is crucial for successful treatment. Regular visits to your dentist can help intercept gum problems before they escalate. If you notice any symptoms, schedule an appointment as soon as possible. Remember, a proactive approach to your dental health can save you time, discomfort, and expense in the future.
Conclusion
Understanding what kind of dentist treats gum disease is essential for individuals over 45 who may be at increased risk of this condition. Whether it’s a general dentist for routine care or a periodontist for advanced treatment, seeking help early can lead to better outcomes. Stay informed and proactive about your gum health to preserve your smile for years to come.
Benefits
1. Specialized Knowledge in Periodontology
Specialized Knowledge in Periodontology
When treating gum disease, it’s essential to seek the expertise of a dentist who specializes in periodontology. These specialists undergo extensive training focusing primarily on the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of gum disease and related conditions. This specialized knowledge equips them with advanced techniques and a deeper understanding of how to effectively manage gum health.
Periodontists are skilled in performing various procedures, including:
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning method that removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
- Gum Grafting: A procedure aimed at restoring lost gum tissue.
- Bone Grafting: This helps regenerate bone lost due to advanced gum disease.
- Lase therapy: Use of lasers in treating periodontal diseases, which can result in less pain and quicker recovery.
With their focused training, periodontists can provide targeted interventions that general dentists may not be equipped to handle, leading to better long-term oral health outcomes for patients struggling with gum disease.
2. Early Detection and Intervention
Early Detection and Intervention
One of the most significant advantages of consulting a dentist specializing in gum disease is their ability to detect issues early on. Many patients may not be aware of the initial signs of gum disease, such as gingivitis, which can easily progress to severe conditions if not addressed promptly.
Regular check-ups with a periodontist typically include:
- Thorough Oral Exam: Periodontists have the experience to identify subtle signs of gum disease that a general dentist might overlook.
- X-rays: They may use advanced imaging techniques to assess bone loss around the teeth.
- Periodontal Probing: This involves measuring the depth of the gum pockets to check for inflammation and disease severity.
Early detection allows for **minimally invasive treatments** that can halt the progression of gum disease and improve overall oral health, making regular visits to a periodontist critical for anyone at risk.
3. Comprehensive Treatment Plans
Comprehensive Treatment Plans
Periodontists are adept at creating individualized and comprehensive treatment plans that address not only the symptoms but also the underlying causes of gum disease. This holistic approach ensures that all aspects of oral health are considered, which is essential for effective treatment.
A comprehensive treatment plan may include:
- Behavior Modification: Guidance on quitting smoking or improving oral hygiene habits.
- Nutritional Counseling: Recommendations to promote better gum health through diet.
- Combination Treatments: Use of both surgical and non-surgical methods tailored to the patient’s needs.
This multifaceted approach not only tackles gum disease but also supports overall health, highlighting the importance of personalized care in dentistry.
4. Understanding Systemic Connections
Understanding Systemic Connections
Another crucial benefit of seeing a dentist specializing in gum disease is their understanding of the systemic connections between oral health and overall health. Research has increasingly shown that gum disease can be linked to various systemic conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory issues.
Periodontists are trained to consider how these systemic relationships affect treatment. They often:
- Collaborate with Other Healthcare Providers: If gum disease is linked to another health issue, they may work alongside physicians to provide comprehensive care.
- Educate Patients: They inform patients about the implications of their gum health on their overall well-being.
- Monitor for Progress: Regular follow-ups can help manage any systemic conditions that might be exacerbated by gum disease.
This interconnected understanding allows for a more proactive approach to treatment, ensuring patients receive holistic care that addresses both oral and systemic health concerns.
5. Advanced Technology and Techniques
Advanced Technology and Techniques
Periodontists have access to the latest technology and techniques in dental care, which can greatly enhance the treatment and management of gum disease. These advancements play a vital role in improving patient outcomes, enhancing comfort, and reducing recovery time.
Some advanced technologies employed by periodontists include:
- Digital Scanning: For precise treatment planning and improved diagnostics.
- 3D Imaging: Allows for thorough assessment and planning of surgical procedures.
- Laser Treatments: Minimally invasive methods that promote quicker healing compared to traditional techniques.
- Regenerative Techniques: Innovations like PRP (platelet-rich plasma) therapy to promote healing in periodontal tissues.
All these tools enable periodontists to deliver top-quality care tailored to each patient’s needs, making visits to these specialists a wise choice for anyone facing gum disease challenges.
Related Links
FAQ – Questions and Answers
What kind of dentist treats gum disease?
Gum disease is treated by general dentists for mild cases and by periodontists—specialists in gum health—for moderate to severe conditions.
What is a periodontist?
A periodontist is a dentist who specializes in preventing, diagnosing, and treating gum disease, and performs procedures like gum grafts and bone regeneration.
When should I see a periodontist instead of a general dentist?
You should see a periodontist if you have advanced gum disease, persistent gum inflammation, or bone loss around the teeth.
What are the early signs of gum disease?
Early signs include red, swollen, or bleeding gums, bad breath, receding gums, and tooth sensitivity.
Can a general dentist treat gum disease?
Yes, general dentists can treat mild gum disease and provide deep cleanings like scaling and root planing.
What procedures do periodontists perform?
Periodontists perform procedures such as flap surgery, gum grafts, bone grafting, and laser therapy for gum disease.
What is scaling and root planing?
It is a deep cleaning method that removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smooths root surfaces to promote healing.
How is gum disease diagnosed?
Dentists diagnose gum disease through oral exams, probing gum pockets, checking for inflammation, and taking X-rays for bone loss.
Is gum disease reversible?
Early-stage gum disease (gingivitis) is reversible with professional treatment and good oral hygiene; advanced periodontitis is manageable but not reversible.
What is flap surgery?
Flap surgery involves lifting the gums to remove deep tartar deposits and suturing them back to reduce pocket depth.
Do periodontists use lasers for treatment?
Yes, many periodontists use laser therapy to treat gum disease with minimal discomfort and faster healing times.
Can untreated gum disease affect overall health?
Yes, untreated gum disease is linked to heart disease, diabetes, respiratory problems, and other systemic health issues.
How do I know if I need gum disease treatment?
If you notice symptoms like bleeding gums, loose teeth, or persistent bad breath, you should consult a dentist or periodontist.
What is periodontal probing?
Periodontal probing measures the depth of the pockets between your teeth and gums to assess the severity of gum disease.
Are antibiotics used in gum disease treatment?
Yes, antibiotics may be prescribed in gel or oral form to help eliminate bacteria and support healing during gum treatment.
What causes gum disease?
Gum disease is caused by plaque buildup, poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, and certain health conditions like diabetes.
Can I prevent gum disease?
Yes, you can prevent gum disease by brushing and flossing daily, avoiding tobacco, and visiting your dentist regularly for cleanings.
Is gum disease treatment painful?
Most treatments are done under local anesthesia, and discomfort is minimal with modern techniques like laser therapy.
How long does gum disease treatment take?
Treatment duration varies based on severity but may involve several appointments over a few weeks to months.
What is a bone graft in periodontal treatment?
A bone graft rebuilds bone lost due to gum disease, supporting the teeth and improving outcomes for advanced cases.
What is tissue grafting?
Tissue grafting replaces lost gum tissue using donor tissue or synthetic material to cover exposed roots and improve gum health.
Can gum disease be hereditary?
Yes, genetic factors can increase susceptibility to gum disease, making regular dental care even more important.
What are periodontal pockets?
Periodontal pockets are spaces that form between the teeth and gums as disease progresses, often indicating the need for treatment.
Do periodontists offer preventive care?
Yes, periodontists provide education, cleanings, and monitoring to help patients prevent progression of gum disease.
How often should I visit the dentist for gum health?
Visit your dentist at least twice a year, or more frequently if you’re at risk for or diagnosed with gum disease.
Is gum disease more common after age 45?
Yes, gum disease risk increases with age, especially for adults over 45 due to long-term plaque exposure and health factors.
Can smoking worsen gum disease?
Yes, smoking reduces blood flow to the gums, impairs healing, and significantly increases the severity of gum disease.
How much does gum disease treatment cost?
Costs vary by severity and provider, ranging from $200 for deep cleaning to $3,000+ for advanced surgical procedures.
Should I see a periodontist even if I have no symptoms?
If you have risk factors or a history of gum issues, regular visits to a periodontist can help with early detection and prevention.
What questions should I ask my periodontist?
Ask about treatment options, recovery time, prevention tips, and how your overall health may affect your gum disease.
Interesting Links
Social Media
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/newofficialwellness/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/people/Well-Health-Guide
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/officialwellness